- All
- View alot
- Often encountered
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
All indirect taxes, if any, are not part of the sales and other income and deductions.
Reply:
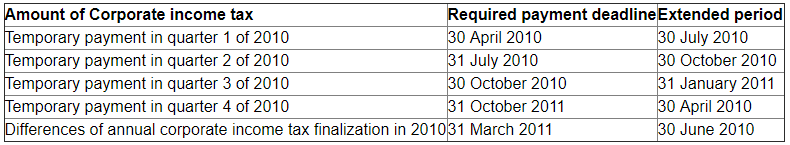
According to the guidance in the Official Letter No. 4283 / BTC-TCT dated 08/4/2010 of the General Department of Taxation, in the case mentioned above, the company is allowed to offset the overpaid tax amount with the outstanding tax amount. In cases where the overpaid tax amounts are larger than the outstanding tax amounts, the companies shall make advance advances for tax reimbursement to overpaid persons and then refund procedures from the budget. If the outstanding tax amount is larger than the overpaid tax amount, the Company shall immediately pay the outstanding tax amount to the State Budget within the prescribed time limit.
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
All indirect taxes, if any, are not part of the sales and other income and deductions.
Reply:
According to the guidance in the Official Letter No. 4283 / BTC-TCT dated 08/4/2010 of the General Department of Taxation, in the case mentioned above, the company is allowed to offset the overpaid tax amount with the outstanding tax amount. In cases where the overpaid tax amounts are larger than the outstanding tax amounts, the companies shall make advance advances for tax reimbursement to overpaid persons and then refund procedures from the budget. If the outstanding tax amount is larger than the overpaid tax amount, the Company shall immediately pay the outstanding tax amount to the State Budget within the prescribed time limit.
Reply:
Reply:

- All
- View alot
- Often encountered
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
The cash equivalent must be the original term of not more than 3 months, excluding the remaining term. Cash equivalents are initially classified as non-reclassification of a short-term investment into cash equivalents.
Reply:
If the Company has advance payment for employees to buy shares of the Company, the company should proceed to lend money (accounting in Account 1388) rather than the procedures for advance (accounted in 141) . If the employee is still working at the Company and has not yet repaid the loan, the Company is not allowed to make provision for bad debts. If the Company appropriates provision for doubtful debts on this debt, this provision shall not be included in the deductible expenses upon determination of taxable income.
Reply:
According to the regulations of the Ministry of Finance's Circular No. 244/2009 / TT-BTC dated December 31, 2009, in this case, the Company (investor) only monitors the number of additional shares on the Report Note. The financial statement, recognizing the value of the received shares, not recording the financial income and not recording the increase in the value of the investment.
Reply:
Whether or not a re-review of prepay or prepayment depends on whether the items meet the definition of monetary items denominated in foreign currencies. If there is no evidence that the contract can not be continued, the advance party shall have the right and the advance party shall be obliged to make payment in the form of goods or services. As such, these items are not monetary items of foreign currency origin and are not revalued.
For receivable bad debts in foreign currency, it is still necessary to re-evaluate, although then continue to make provisions because these are two different issues. Debt becomes hard does not mean the unit loses the right to be revoked. If not re-evaluated does not reflect the right of the unit. If no backup will not reflect the possibility of loss. It is not appropriate to assume that the interest earned from the revaluation will be offset against the reserve costs. VAS and IFRS have no restrictions on not re-evaluating currency items becoming bad debts.
Reply:
Losses should be recorded directly as expenses in the statement of income. Recognition of a loss as an asset (long-term prepayment) is not consistent with the nature of the financial and accounting principles.
Note that some cases where the exchange rate losses are posted on the PSC, must be directly allocated from Account 413 to Account 635, and must not be recorded as Debt 242 / Yes 413.
Reply:
Exchange rate differences are not capitalized as borrowing costs. The cases of exchange rate differences recorded in the accounting committee include:
- Conversion of financial statements in VND to VND in VND;
- Due to the permission of the Prime Minister;
- Exchange rate difference arising in the pre-operation period of security and defense enterprises.
Reply:
Original prices of imported goods include purchase price and other directly related costs. Customs only publish rates for tax purposes and these taxes are only one of the cost factors that constitute the cost. Therefore, it is not possible to apply the Customs rate to the purchasing unit. On the other hand, the time of recognition of assets may not be the time of customs clearance, so it is not possible to take the Customs rate for conversion when the asset is recognized.
Reply:
Circular 53 allowed the application of the actual exchange rate to be credited to the FI, D / A; Debtors must pay. At the end of the period, after re-evaluating the original balance on the A / Cs, based on the exchange rate difference between the Credit Party and the creditors of the Account Accounts, the receivables must be recognized once in revenue or financial expenses. .
Reply:
After the Ministry of Finance promulgated Circular No. 53/2016 / TT-BTC of March 21, 2016 amending and supplementing Circular 200, enterprises are allowed to choose exchange rates in a flexible manner. Accordingly, enterprises are allowed to choose the actual transaction rates to record foreign currency transactions according to Circular 200 or to use only one type of exchange rate according to Circular 53 without affecting the financial statements.
Reply:
Circular 200 removes the notion of treating exchange rate differences due to the revaluation of monetary items denominated in foreign currencies. All exchange rate differences resulting from reevaluation are all done, thereby also eliminating the restriction on the prohibition of the distribution of profits to foreign exchange gains by revaluation.
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
The cash equivalent must be the original term of not more than 3 months, excluding the remaining term. Cash equivalents are initially classified as non-reclassification of a short-term investment into cash equivalents.
Reply:
If the Company has advance payment for employees to buy shares of the Company, the company should proceed to lend money (accounting in Account 1388) rather than the procedures for advance (accounted in 141) . If the employee is still working at the Company and has not yet repaid the loan, the Company is not allowed to make provision for bad debts. If the Company appropriates provision for doubtful debts on this debt, this provision shall not be included in the deductible expenses upon determination of taxable income.
Reply:
According to the regulations of the Ministry of Finance's Circular No. 244/2009 / TT-BTC dated December 31, 2009, in this case, the Company (investor) only monitors the number of additional shares on the Report Note. The financial statement, recognizing the value of the received shares, not recording the financial income and not recording the increase in the value of the investment.
Reply:
Whether or not a re-review of prepay or prepayment depends on whether the items meet the definition of monetary items denominated in foreign currencies. If there is no evidence that the contract can not be continued, the advance party shall have the right and the advance party shall be obliged to make payment in the form of goods or services. As such, these items are not monetary items of foreign currency origin and are not revalued.
For receivable bad debts in foreign currency, it is still necessary to re-evaluate, although then continue to make provisions because these are two different issues. Debt becomes hard does not mean the unit loses the right to be revoked. If not re-evaluated does not reflect the right of the unit. If no backup will not reflect the possibility of loss. It is not appropriate to assume that the interest earned from the revaluation will be offset against the reserve costs. VAS and IFRS have no restrictions on not re-evaluating currency items becoming bad debts.
Reply:
Losses should be recorded directly as expenses in the statement of income. Recognition of a loss as an asset (long-term prepayment) is not consistent with the nature of the financial and accounting principles.
Note that some cases where the exchange rate losses are posted on the PSC, must be directly allocated from Account 413 to Account 635, and must not be recorded as Debt 242 / Yes 413.
Reply:
Exchange rate differences are not capitalized as borrowing costs. The cases of exchange rate differences recorded in the accounting committee include:
- Conversion of financial statements in VND to VND in VND;
- Due to the permission of the Prime Minister;
- Exchange rate difference arising in the pre-operation period of security and defense enterprises.
Reply:
Original prices of imported goods include purchase price and other directly related costs. Customs only publish rates for tax purposes and these taxes are only one of the cost factors that constitute the cost. Therefore, it is not possible to apply the Customs rate to the purchasing unit. On the other hand, the time of recognition of assets may not be the time of customs clearance, so it is not possible to take the Customs rate for conversion when the asset is recognized.
Reply:
Circular 53 allowed the application of the actual exchange rate to be credited to the FI, D / A; Debtors must pay. At the end of the period, after re-evaluating the original balance on the A / Cs, based on the exchange rate difference between the Credit Party and the creditors of the Account Accounts, the receivables must be recognized once in revenue or financial expenses. .
Reply:
After the Ministry of Finance promulgated Circular No. 53/2016 / TT-BTC of March 21, 2016 amending and supplementing Circular 200, enterprises are allowed to choose exchange rates in a flexible manner. Accordingly, enterprises are allowed to choose the actual transaction rates to record foreign currency transactions according to Circular 200 or to use only one type of exchange rate according to Circular 53 without affecting the financial statements.
Reply:
All three cases are not required to make provisions for inventory reduction.
Reply:
Circular 200 removes the notion of treating exchange rate differences due to the revaluation of monetary items denominated in foreign currencies. All exchange rate differences resulting from reevaluation are all done, thereby also eliminating the restriction on the prohibition of the distribution of profits to foreign exchange gains by revaluation.
Reply:
Loans have been presented as receivables should be provisioned. Investments held to other maturity are not provisioned but revalued. If there is evidence that part or all of the investment may not be recoverable, the loss to financial expense in the period should be recognized. Where the amount of loss can not be reliably determined, the accountant may not reduce the investment but must explain the recoverability of the investment.
Reply:
A loan is recognized in the PSC when the business is exposed to the risks and benefits of the loan. Thus, only the direct lending business or the new entrusting party is presented on the PSC.
When an enterprise acts as a trustee, a loan is disbursed, the amount disbursed to a third party is not presented as a loan on the PSC.
Reply:
Circular 200 requires weighted average method. However, Circular 53 adds a FIFO methodology to accommodate some software. It means that the enterprise is allowed to choose one of the two methods, but must ensure the most applicable in the whole fiscal year. If there is a change of method in the new fiscal year, it must be disclosed in the financial statements and the comparative information under VAS 29 must be reported.
Reply:
This case needs to be considered since the net present value of the subsidiary is higher than the cost of the parent company's investment. Declining the value of an investment can lead to a negative investment. On the other hand, equity method should not be applied to joint ventures or associates for this case because the value of the previous investment has been increased, but it is now recognized as a reduction. This case should be based on the nature of profit distribution even though the form is to return capital to investors. Therefore, it is important to consider revenue recognition.
Reply:
According to VAS 02, the costs of transportation, storage when buying inventory and storage and transportation costs necessary for the next production (inventory was not completed and ready for sale. When it is finished and ready for sale, it is not included in the original price but it is calculated as the cost of selling whether the goods are sold immediately or not.
Reply:
Construction contractors do not have interest rates for construction works (except for construction works and investors
Reply:
The retail price approach applies to periodic inventory businesses, multiple customers, and a large number of items, such as supermarkets. When sales can not be calculated immediately, but know the sales. This method requires calculating the average normalized profit on sales and inventory value by end-of-the year sales to calculate the cost of goods sold, thereby calculating the end inventory value.
Reply:
- Consumer goods: Reflected right at cost, not recognized revenue, cost
- Must distinguish the Promotion, advertising and donation cases. If without conditions, the value of promotional goods or advertising donations shall be recognized into sale expenses; If the conditions are attached, the turnover and cost price shall be recognized on a case-by-case basis.
Reply:
Reflection in Accounts 152 or 153 is entirely decided by the business as only new businesses know how to use their assets. An asset can be classified as a material in this business but is a device in another enterprise
Reply:
There are no definitions of out-of-pocket losses and the concept is understood in different ways. The Ministry of Finance has allowed some provisions to be made when subsidiary, joint ventures and associates suffer losses without any distinction between internal or external.
Reply:
- For trading securities, make a provision for price decrease.
- For investment in subsidiaries, joint ventures and associates: Making provision for losses due to loss, not making allowance for loss.
- Normal long-term investment (ready-for-sale): If the stock is listed, provision for discount; If the fair value can not be determined, provisions will be made similarly to investments in subsidiaries, joint ventures and associates.
- All
- View alot
- Often encountered
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply:
Reply: